Disseminating Knowledge: The Power Of Sharing Information
Disseminating Knowledge: The Power of Sharing Information
Related Articles: Disseminating Knowledge: The Power of Sharing Information
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Disseminating Knowledge: The Power of Sharing Information. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Disseminating Knowledge: The Power of Sharing Information
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Disseminating Knowledge: The Power of Sharing Information
- 3.1 The Importance of Dissemination: Unlocking Potential
- 3.2 Methods of Dissemination: A Multifaceted Approach
- 3.3 Challenges and Considerations: Navigating a Complex Landscape
- 3.4 Strategies for Effective Dissemination: Ensuring Impact
- 3.5 FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
- 3.6 Conclusion: A Shared Responsibility
- 4 Closure
Disseminating Knowledge: The Power of Sharing Information

The act of making information known, or dissemination, is a fundamental pillar of human progress. It fuels innovation, fosters understanding, and empowers individuals and societies to navigate a complex world. This article delves into the multifaceted nature of information dissemination, exploring its significance, methods, challenges, and ethical considerations.
The Importance of Dissemination: Unlocking Potential
The act of sharing information unlocks a wealth of benefits, impacting individuals, communities, and the world at large.
- Empowerment and Informed Decision-Making: Access to accurate and relevant information empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their lives, health, finances, and civic participation.
- Knowledge Creation and Innovation: Sharing research findings, scientific discoveries, and technological advancements fuels innovation and drives societal progress.
- Social Cohesion and Understanding: Disseminating diverse perspectives and fostering open dialogue promotes understanding, empathy, and social cohesion.
- Addressing Global Challenges: Sharing information on environmental issues, health crises, and humanitarian concerns facilitates collective action and helps address global challenges.
Methods of Dissemination: A Multifaceted Approach
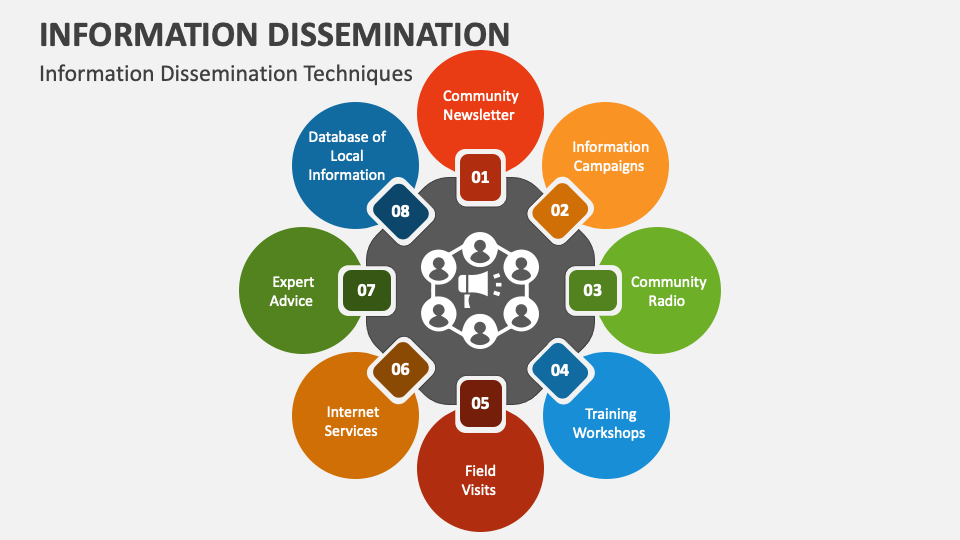
Information dissemination occurs through a wide range of channels, each with its own strengths and limitations.
Traditional Media: Newspapers, magazines, radio, and television have historically been the primary avenues for disseminating information to a broad audience. While their reach is vast, they are often subject to editorial biases and limited interactivity.
Digital Platforms: The internet has revolutionized information dissemination, offering unprecedented accessibility and speed. Websites, social media platforms, blogs, and online forums allow for the rapid sharing of information and facilitate global communication.
Educational Institutions: Schools, universities, and libraries play a crucial role in disseminating knowledge through formal education, research, and access to resources.
Government Agencies: Governments utilize various channels to disseminate information related to public policy, regulations, and public safety.
Non-Profit Organizations: Advocacy groups, research institutions, and humanitarian organizations utilize dissemination strategies to raise awareness, mobilize support, and promote social change.
Community Networks: Local communities often rely on informal networks, such as community centers, neighborhood groups, and word-of-mouth, to share information and foster local engagement.
Challenges and Considerations: Navigating a Complex Landscape
While the benefits of information dissemination are undeniable, it is important to acknowledge the challenges and ethical considerations associated with this process.
- Information Overload: The sheer volume of information available in the digital age can lead to information overload, making it difficult to filter out reliable and relevant content.
- Misinformation and Disinformation: The ease with which information can be shared online has fueled the spread of misinformation and disinformation, posing significant risks to public discourse and societal stability.
- Bias and Manipulation: Information can be intentionally manipulated or presented in a biased way to influence public opinion or advance specific agendas.
- Digital Divide: Unequal access to technology and digital literacy can exacerbate existing inequalities and limit the reach of information dissemination efforts.
Strategies for Effective Dissemination: Ensuring Impact
To ensure effective information dissemination, it is essential to adopt strategies that address the challenges mentioned above.
- Verification and Fact-Checking: Prioritize the dissemination of accurate and reliable information by verifying sources and employing fact-checking techniques.
- Promoting Media Literacy: Encourage critical thinking skills and media literacy to help individuals navigate the information landscape and identify credible sources.
- Diversity of Perspectives: Seek out and share diverse perspectives to foster balanced and informed discussions.
- Accessibility and Inclusivity: Make information accessible to all audiences, including those with disabilities, language barriers, and limited access to technology.
- Transparency and Accountability: Be transparent about sources, funding, and potential biases to maintain trust and credibility.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: What are the key elements of effective information dissemination?
A: Effective information dissemination requires a multi-pronged approach that prioritizes accuracy, clarity, accessibility, and engagement. It involves understanding the target audience, choosing appropriate channels, crafting compelling messages, and fostering ongoing dialogue.
Q: How can individuals contribute to the dissemination of accurate information?
A: Individuals can contribute by:
- Fact-checking information before sharing it.
- Supporting independent and reliable news sources.
- Challenging misinformation and disinformation when encountered.
- Engaging in respectful and informed discussions online.
Q: What are the ethical implications of information dissemination?
A: Ethical considerations include:
- Respecting privacy and confidentiality.
- Avoiding the spread of harmful or offensive content.
- Ensuring transparency and accountability.
- Promoting access to information for all.
Q: How can technology be used to address the challenges of information dissemination?
A: Technology can play a crucial role in:
- Developing tools for fact-checking and detecting misinformation.
- Creating platforms for collaborative knowledge creation and dissemination.
- Improving access to information for underserved communities.
Conclusion: A Shared Responsibility
Disseminating information effectively is a shared responsibility. It requires a collective commitment to promoting accuracy, fostering critical thinking, and ensuring equitable access to knowledge. By embracing ethical practices and leveraging technology responsibly, we can unlock the full potential of information to empower individuals, foster understanding, and drive positive change in the world.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Disseminating Knowledge: The Power of Sharing Information. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!